ClearWaste

To restore nature through green technology

A household of 2 children generates as estimated waste between:
0.11 – 4.54kg /day

The municipal budget for waste management is often:
20 – 50%

Operating cost of waste management are estimated at:
US$35 – US$100/ton
The world generates 1.3 billion TON of waste per year.
By 2050, this amount will reach 3.5 billion TON per year.
and
67% of the world’s waste is not treated
33% of waste is disposed at landfills and incineration plants
All these crisis are interrelated and can be resolved through EFFECTIVE & EFFICIENT WASTE MANAGEMENT
SOLUTION

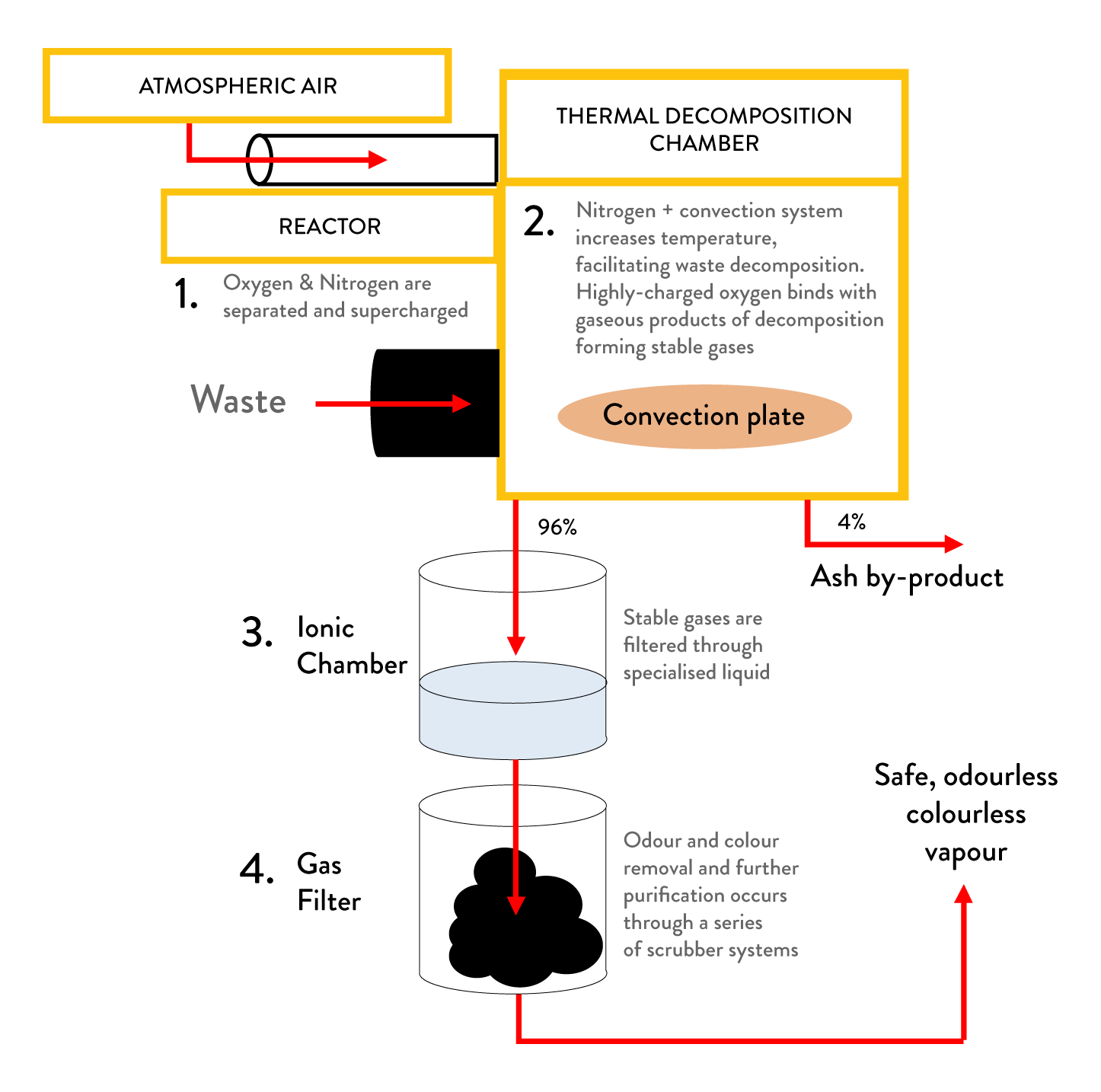
The ClearWaste is a low-cost and modular unit that converts various forms of waste into useful byproducts such as fertilisers and construction materials.
Unlike incinerators, the ClearWaste does not operate on fuel, nor does it generate harmful ash and emissions.
The ClearWaste runs on renewables to drive an environmentally friendly decomposition process.

Process
ClearWaste Models
Bare Unit
Green: ClearWaste™ requires no fuel and releases no harmful emissions
- Low operations & maintenance cost
- Modular & mobile
- Self-sustainable
- Safe & user-friendly
- Robust
- Durable
Containerised Unit

Green: ClearWaste™ requires no fuel and releases no harmful emissions
- Low operations & maintenance cost Modular & mobile
- Self-sustainable
- Safe & user-friendly
- Robust
- Durable
- Specially designed container
- ClearWaste hydraulic powered side door with lifting time less than 30 seconds
- Open to top side door; complimentary feature to work as a shed which is useful for an outdoor environment
Trailer Mounted Unit

Green: ClearWaste™ requires no fuel and releases no harmful emissions
- Low operations & maintenance cost Modular & mobile
- Self-sustainable
- Safe & user-friendly
- Robust
- Durable
- Specially designed container
- ClearWaste hydraulic powered side door with lifting time less than 30 seconds
- Drop down side door that works as a platform for daily routine. It can withstand a 500kg load at one time
To Know More About ClearWaste Call: +91 94432 34266
Knowledge Center
Waste recycling, while generally considered environmentally beneficial, can still have some negative impacts in terms of emissions. Here are some explanations of potentially harmful emissions associated with waste recycling.
Types Of Emissions
- Air emissions from incineration: Incineration of waste also releases emissions into the air, including greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane, as well as pollutants like nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, and particulate matter. These emissions can contribute to air pollution, which can have negative impacts on human health, such as respiratory issues and other health problems, as well as contribute to climate change by increasing greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere.
- Emissions from recycling processes: Recycling processes can also generate emissions, depending on the specific methods used. For example, some recycling processes may require energy-intensive activities like transportation, shredding, and melting, which can result in emissions of greenhouse gases and air pollutants. Additionally, some recycling processes may involve the use of chemicals or other substances that can be harmful to human health or the environment if not properly managed.
- Ash from biomass waste: Biomass waste, such as agricultural residues or wood, is sometimes used as a source of renewable energy through processes like combustion or gasification. However, the ash generated from biomass waste can contain high levels of nutrients like phosphorus and potassium, which can potentially cause water pollution if not properly managed. Runoff from ash disposal sites can contaminate nearby water bodies, leading to eutrophication, which is the excessive growth of algae that can harm aquatic ecosystems.
- Contamination of recyclable materials: Recycling can sometimes lead to contamination of recyclable materials, which can result in emissions of harmful substances. For example, if recyclable materials are contaminated with non-recyclable items or hazardous substances, such as chemicals or oils, the recycling process may generate emissions of pollutants when attempting to separate or process the contaminated materials.
Conclusion
It’s important to note that the potential harmful emissions associated with waste recycling can be mitigated through proper management practices, such as effective air pollution control technologies, appropriate handling and disposal of ash, careful selection of recycling processes, and strict monitoring and regulation of waste management facilities. Additionally, focusing on reducing waste generation at the source and promoting sustainable waste management practices, such as waste reduction, reuse, and composting, can also help minimise the negative impacts of waste recycling. Overall, careful planning, regulation, and monitoring are essential in ensuring that waste recycling is done in an environmentally responsible manner.
Always consult with local waste management regulations and guidelines to ensure proper handling and disposal of waste materials. Environmental protection and human health should always be a priority in waste management practices. Remember to reduce, reuse, and recycle whenever possible to minimise the negative impacts of waste on our environment. Consideration of the entire life cycle of waste management is important in order to make informed decisions and minimise potential harmful emissions associated with waste recycling.
It’s important to seek guidance from qualified professionals and comply with all applicable laws and regulations related to waste management in your area. Protecting the environment and human health should always be a priority in waste management practices. If you have questions or concerns about waste recycling or its potential impacts, it’s best to consult with local waste management authorities or environmental experts for guidance.

